World War II saw women stepping into a broad spectrum of occupations in both military and civilian capacities.
- Blogs
- World War Ii
- Womens Pivotal Roles In Wwii 66322746bdccdd0001d2da50
Women's Pivotal Roles in WWII
World War II • 1 May, 2024 • 6,630 Views • ⭐ 5.0
Written by Shivani Chourasia

It's difficult to determine the exact figure, but World War II had a higher number of combatants than any war before, with estimates ranging between 70 million and 100 million participants. This exceeded the numbers from World War I. The massive demand for manpower opened significant opportunities in all sectors, whether in civilian life or military engagements. Women rapidly filled these vacancies. Beyond conventional roles such as nursing or administrative duties, many women took on positions as welders, drivers, aviators, and even as combatants.
Echoes of the Past

World War I was the first conflict where women began to fill roles traditionally held by men, including non-combative roles like clerical work, driving, nursing, and even in hazardous positions. In the UK, women working in ammunition production were nicknamed “Munitionettes.” The subsequent global conflict of World War II required an even greater female workforce than the previous global conflict. Women in the thousands sought work to support the war effort.
WORLD WAR II QUIZ • 10 QUESTIONS • 2 MINS
We've got a World War II quiz for you!
TAP TO PLAY

Evolving Roles in a New Conflict

The roles women occupied varied significantly from one country to another, largely due to differing national attitudes. Some countries, like the United Kingdom and the United States, prohibited women from engaging in combat. Conversely, the Soviet Union welcomed women in combat roles, with many serving as pilots, sharpshooters, and tank crew members. In terms of industrial employment, statistics are telling. In the United States, about 19 million women were employed, making up thirty-six per cent of the workforce in sectors such as munitions, chemicals, and machinery. In contrast, Nazi ideology strictly limited women to traditional roles centred on domesticity and motherhood. Nevertheless, the exigencies of war compelled the inclusion of thousands of women in diverse roles ranging from domestic aides to prison wardens, and agricultural workers.
Technological Advancements and New Opportunities
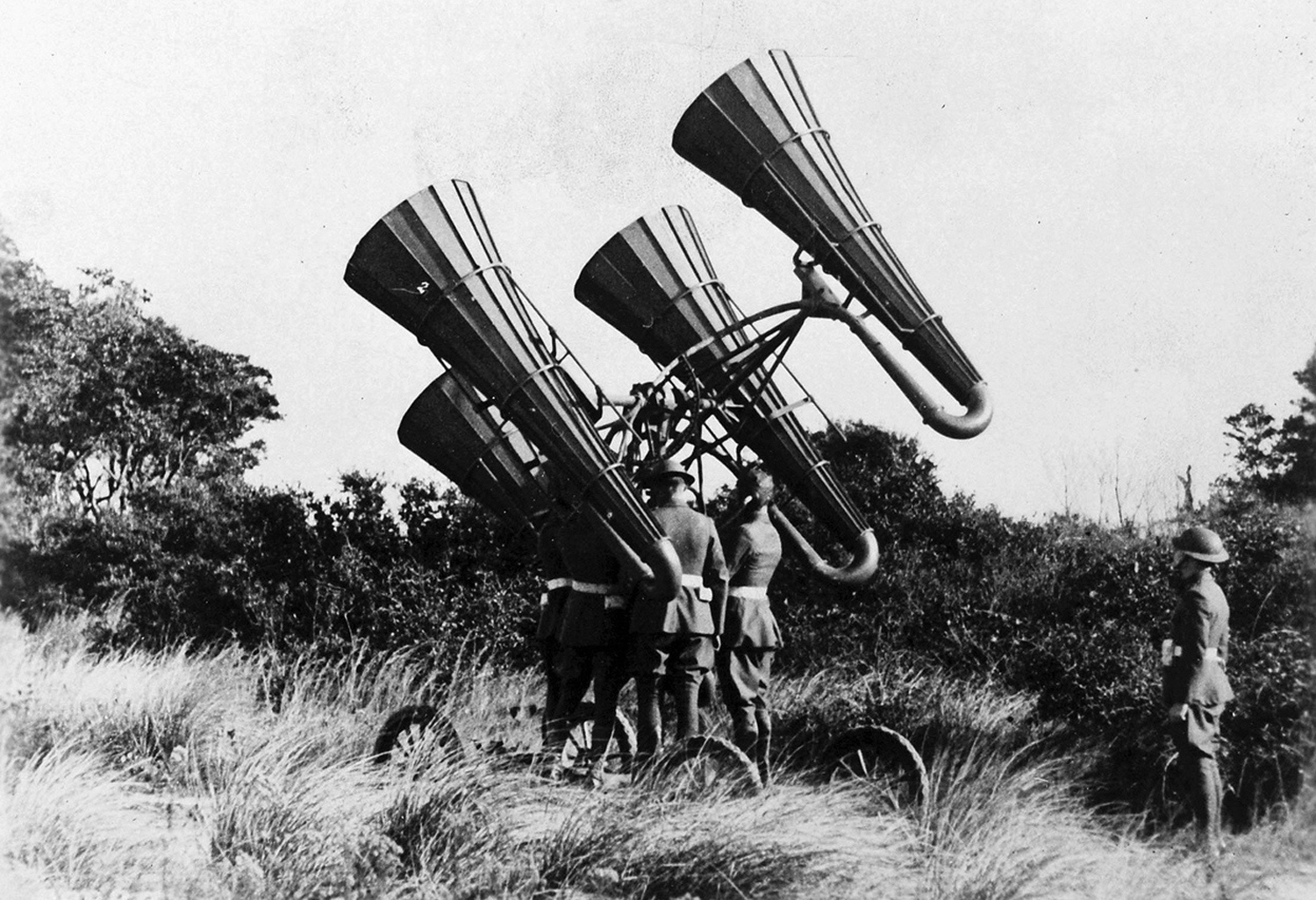

World War II opened up opportunities for women that were unavailable during World War I. Innovations such as radar technology and the urgent needs of war led to the opening of many previously inaccessible roles. Despite the advancements, a common rule persisted in all Western nations: women were excluded from direct combat roles.
Women's Expanded Roles in the RAF and Beyond

In 1940, the advent of radar technology provided new opportunities for women in the Royal Air Force, where they served as plotters and air traffic controllers, directing night fighters to their targets. These women, often officers, were well-trained and skilled. They also participated in anti-aircraft units, handling both guns and searchlights, a stark contrast to the aviation-free skies of the Great War. The U.S. was the only nation not targeted by bombers. In the UK alone, 190,000 women joined the RAF, thereby releasing men for frontline duties.
HISTORY QUIZ • 10 QUESTIONS • 2 MINS
We've got a History quiz for you!
TAP TO PLAY

During World War I, women were excluded from flying, but by the Second World War, perceptions had shifted. Starting in 1939, both the Royal Air Force and the U.S. Army Air Force formed two groups—the Air Transport Auxiliary (ATA) and the Women Airforce Service Pilots—requiring a minimum of one hundred hours of flight training. These women pilots undertook tasks such as ferrying aircraft for repairs, towing targets, and performing flight checks, thus allowing male pilots to engage in combat roles.
Industrial Contributions by Women

The war effort necessitated a substantial increase in women's participation in industrial roles compared to World War I, with women taking up positions as mechanics, riveters, and welders in shipyards and factories. Women also became indispensable in roles like canteen workers. With the labour shortages, munitions production—always busy and perilous—became predominantly a woman's job.
The Manhattan Project and Women's Roles

Women also played a crucial but less publicized role in the Manhattan Project, the initiative to develop the atomic bomb. Beyond typical administrative roles, women served as technicians, lab workers, and even scientists. Notable among them were Lilli Hornig, whose recommendations influenced the decision to conduct A-bomb tests in desert rather than populated areas, and Chieng-Shung Wu, who also contributed significantly to the project.
Women in Combat and Intelligence

While many women served stateside, others, like American and British nurses, were stationed just behind the front lines, where they treated wounded soldiers, sometimes at the cost of their own lives. In the Soviet Union and other occupied territories, women were allowed to engage directly in combat, facing the same dangers as male soldiers, including death and capture. Soviet women were particularly prominent, with numerous female soldiers and snipers, and women pilots in the Red Air Force who completed 30,000 sorties and produced celebrated fighter aces. Women also served as intelligence agents, undertaking highly dangerous missions that included parachuting behind enemy lines and engaging in direct combat. Like their male counterparts, these women faced extreme risks, including torture and death.
Global Perspective of WW2

World War II was not just fought by the major powers, but involved contributions from women across the globe, showcasing a diverse array of roles in multiple contexts. In countries like Canada, women joined the Canadian Women's Army Corps, where they worked as mechanics, drivers, and clerks. Australia saw the establishment of the Women's Auxiliary Australian Air Force, where women engaged in roles ranging from wireless telegraphy to aircraft maintenance.
In Asia, Chinese women played vital roles both on the home front and in direct support of military operations, serving as nurses, air raid wardens, and in some instances, soldiers. In countries under colonial rule, such as India, women contributed to the war effort through the Indian Women's Auxiliary Corps, where they served in non-combat roles that were crucial to the Allied war strategy. The contributions of these women not only highlight the global nature of the war effort but also demonstrate the universal shift towards recognizing women's capabilities in diverse and challenging roles.
Resistance Movements by Women in WW2
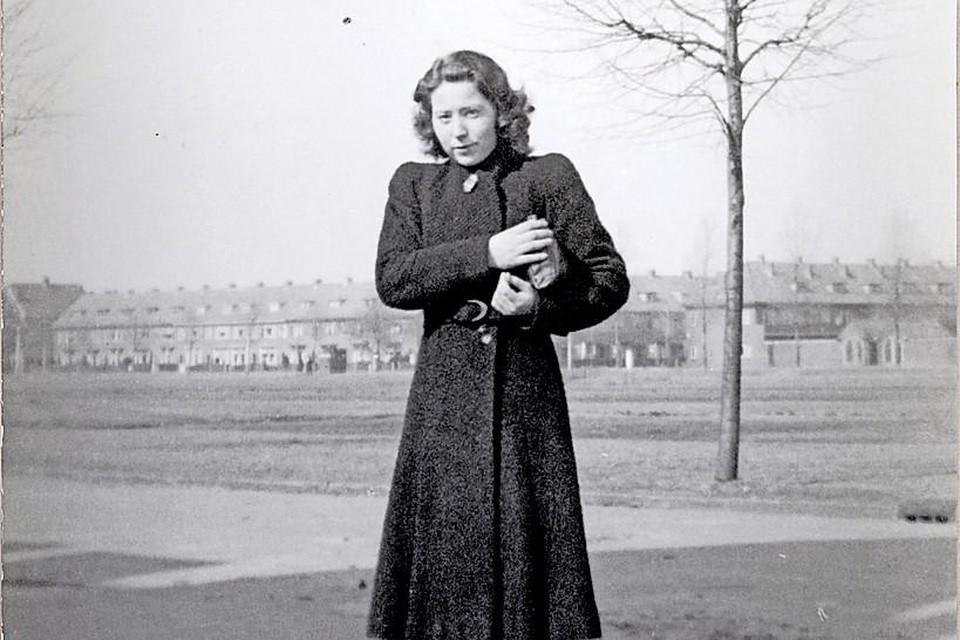

Throughout occupied Europe, women took to clandestine operations and resistance movements to thwart Axis powers. In France, women like Lucie Aubrac and the iconic figure of the French Resistance, Simone Segouin, played critical roles. They participated in sabotage missions, produced underground newspapers, and helped downed Allied airmen escape capture.
In the Netherlands, women like Hannie Schaft became symbols of resistance, engaging in direct actions against German occupiers, from sabotage to assassinations. Similarly, in Poland, the Home Army counted numerous women among its ranks, who acted as couriers, nurses, and intelligence gatherers, proving instrumental to the Warsaw Uprising and other key resistance efforts.
These resistance movements were not only crucial to the military outcomes of World War II but also marked a significant moment in the history of women in warfare. They showed that women could organize, plan, and execute missions with the same skill and determination as their male counterparts.
Conclusion
World War II marked a profound shift in societal roles, breaking down barriers and redefining the contributions of women. Across continents and cultures, women stepped up in unprecedented ways, from the battlefields to the factories, from clandestine operations to groundbreaking scientific research. Their bravery, resilience, and innovation not only shaped the outcome of the war but also forged a legacy of strength and capability that would influence generations to come. This era highlighted the undeniable impact and importance of women in shaping our world.
Test your knowledge of History! Visit: https://4799.play.quizzop.com/history-quiz/category
Rate this article
Other articles you may like
Europe's 7 Most Significant War Memorials
History • 4 Sept, 2023 • 68,122 Views

6 Traditional Dances from Africa and Where to Witness Them
History • 24 Aug, 2023 • 42,902 Views

5 Iconic Museums of Modern Art in the World
History • 14 Aug, 2023 • 69,431 Views

Top 5 Cities with Impressive Streets in the World
History • 14 Aug, 2023 • 67,108 Views

7 Architectural Wonders of the Middle East
History • 14 Aug, 2023 • 67,613 Views